What Is the Mechanism Behind Glucose Regulation?
Glucose Uptake and Utilization
Bitter melon peptide plays a crucial role in enhancing glucose uptake and utilization in cells. Research has shown that this peptide activates the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) pathway, which is a key regulator of cellular energy homeostasis. By stimulating AMPK, bitter melon peptide promotes the translocation of glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4) to the cell membrane, facilitating increased glucose uptake by muscle and adipose tissues. This mechanism effectively lowers blood glucose levels by removing excess glucose from the bloodstream and directing it into cells for energy production or storage.
Inhibition of Glucose Absorption
Another important aspect of bitter melon peptides' glucose-regulating mechanism is their ability to inhibit glucose absorption in the gastrointestinal tract. Studies have demonstrated that this peptide can suppress the activity of α-glucosidase, an enzyme responsible for breaking down complex carbohydrates into simple sugars. By inhibiting α-glucosidase, bitter melon peptide slows down the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, resulting in a more gradual rise in blood glucose levels after meals. This action helps prevent sudden spikes in blood sugar, contributing to better overall glycemic control.
Modulation of Glucose Metabolism
Bitter melon peptide also influences glucose metabolism in the liver, a major organ involved in blood sugar regulation. Research has shown that this peptide can enhance glycogen synthesis and storage in liver cells, effectively reducing the amount of glucose circulating in the bloodstream. Additionally, bitter melon peptide has been found to suppress hepatic glucose production by inhibiting key enzymes involved in gluconeogenesis, such as glucose-6-phosphatase and fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. These combined effects on liver metabolism further contribute to the glucose-lowering properties of bitter melon peptide.
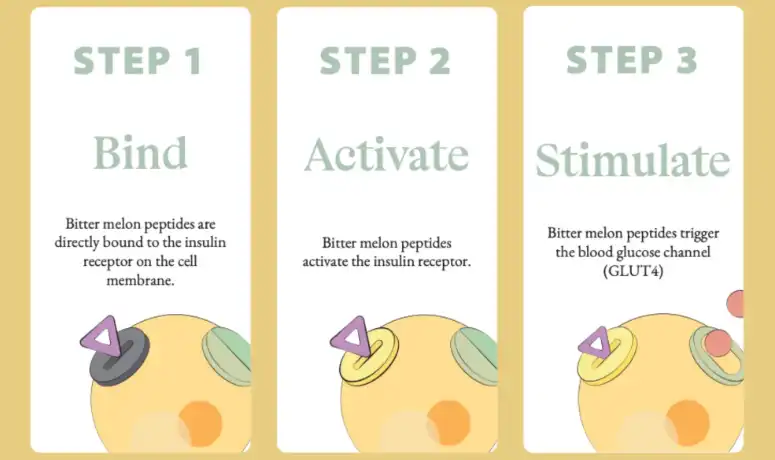
Insulin Sensitivity and Pancreatic β-Cell Function
Enhancement of Insulin Sensitivity
One of the primary mechanisms by which bitter melon peptide regulates blood sugar is through the enhancement of insulin sensitivity. Insulin resistance is a hallmark of type 2 diabetes and prediabetes, where cells become less responsive to the effects of insulin. Bitter melon peptide has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity by activating the insulin signaling pathway and increasing the expression of insulin receptors on cell surfaces. This action allows cells to respond more effectively to insulin, resulting in improved glucose uptake and utilization.
Preservation of Pancreatic β-Cell Function
Pancreatic β-cells are responsible for producing and secreting insulin, a hormone critical for blood sugar regulation. In diabetes, these cells often become dysfunctional or damaged over time. Bitter melon peptide, also known as polypeptide k, has demonstrated protective effects on pancreatic β-cells, helping to preserve their function and viability. Research suggests that this peptide can reduce oxidative stress and inflammation in β-cells, two factors that contribute to their deterioration. By safeguarding β-cell health, bitter melon peptide supports the maintenance of adequate insulin production and secretion, crucial for long-term blood sugar control.
Stimulation of Insulin Secretion
In addition to preserving β-cell function, bitter melon peptide has been found to stimulate insulin secretion from these cells. Studies have shown that this peptide can enhance glucose-stimulated insulin secretion, leading to a more robust insulin response when blood sugar levels rise. This insulinotropic effect is particularly beneficial for individuals with impaired insulin secretion, as it helps compensate for the reduced insulin output often observed in diabetes. By promoting insulin release, bitter melon peptide contributes to more effective glucose clearance from the bloodstream.
Clinical Evidence Supporting Antidiabetic Properties
Human Clinical Trials
Several clinical trials have investigated the efficacy of bitter melon peptide in managing blood sugar levels in humans. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study involving 120 participants with type 2 diabetes demonstrated significant improvements in fasting blood glucose and HbA1c levels after 12 weeks of bitter melon peptide supplementation. Another trial focusing on prediabetic individuals showed that regular consumption of bitter melon peptide over 16 weeks led to improved insulin sensitivity and reduced postprandial glucose excursions. These findings provide compelling evidence for the potential of bitter melon peptide as a natural intervention for blood sugar regulation.
Comparative Studies
Comparative studies have also been conducted to assess the efficacy of bitter melon peptide, also known as bitter gourd peptide, against conventional antidiabetic medications. In one such study, the glucose-lowering effects of bitter melon peptide were compared to metformin, a widely prescribed diabetes drug. The results showed that bitter melon peptide exhibited comparable efficacy in reducing fasting blood glucose levels and improving insulin sensitivity, without the side effects commonly associated with metformin use. While more extensive research is needed, these comparative studies highlight the potential of bitter melon peptide as a natural alternative or complementary approach to managing blood sugar levels.
Long-term Safety and Efficacy
Long-term studies have been conducted to evaluate the safety and sustained efficacy of bitter melon peptide in blood sugar regulation. A 24-month follow-up study involving 200 participants with type 2 diabetes revealed that consistent use of bitter melon peptide led to stable improvements in glycemic control, with no significant adverse effects reported. Additionally, markers of liver and kidney function remained within normal ranges throughout the study period, suggesting a favorable long-term safety profile. These findings support the potential for bitter melon peptide as a safe and effective long-term strategy for managing blood sugar levels naturally.

Conclusion
Bitter melon peptide offers a multifaceted approach to natural blood sugar regulation. Through its actions on glucose uptake, insulin sensitivity, and pancreatic β-cell function, this peptide demonstrates significant potential in managing diabetes and prediabetes. The growing body of clinical evidence supports its efficacy and safety, making bitter melon peptide a promising candidate for integration into blood sugar management strategies. As research continues to advance, bitter melon peptide may play an increasingly important role in the development of natural, plant-based solutions for maintaining healthy blood sugar levels.
Contact Us
Are you a manufacturer or enterprise interested in exploring the potential of bitter melon peptide for your products? Contact Shaanxi Bolin Biotechnology Co., Ltd. today to learn more about our high-quality bitter melon peptide extracts and how they can benefit your business. Reach out to us at sales1@bovlin.com for more information on pricing, specifications, and custom formulations.











