What's Inside Green Tea Extract Powder?
Green tea extract powder contains a complex matrix of bioactive compounds, primarily polyphenols, which account for 30-40% of its dry weight. The most significant components include catechins like EGCG (epigallocatechin gallate), comprising up to 60% of total catechins, along with caffeine (1-5%), L-theanine, and various vitamins and minerals. Manufacturers value this concentrated botanical ingredient for its standardized polyphenol content, typically ranging from 50% to 98% depending on extraction methods. The powder also contains chlorophyll, proteins, lipids, and trace elements that contribute to its functional properties. These naturally occurring compounds work synergistically, making green tea extract a versatile ingredient for nutraceutical, cosmetic, and functional food formulations worldwide.
Key Nutrients and Active Phytochemicals in Green Tea Extract
Primary Polyphenolic Compounds
Green tea extract powder derives its potency from an exceptional concentration of polyphenolic compounds. These bioactive molecules represent the foundation of its functional properties in industrial applications. The total polyphenol content in quality extracts typically exceeds 90% when properly standardized.
Catechins dominate the polyphenol profile, with four major types present. EGCG (epigallocatechin gallate) accounts for 50-60% of total catechins. EGC (epigallocatechin) follows at 15-20%, while ECG (epicatechin gallate) comprises 10-15%. Simple epicatechin accounts for 5-10% of the catechin fraction. These percentages vary based on cultivation conditions and processing methods.
Manufacturing facilities prioritize consistent polyphenol profiles for product standardization. The extraction process significantly influences the final composition. Water-based extraction yields different ratios than ethanol-based methods. Temperature control during processing preserves heat-sensitive compounds. Quality organic green tea extract powder maintains optimal polyphenol integrity through careful handling.
Furthermore, flavonols like quercetin, kaempferol, and myricetin enhance the antioxidant capacity. These secondary metabolites contribute approximately 2-3% of total dry weight. Their presence indicates premium raw material selection and gentle processing techniques.
Methylxanthines and Alkaloid Content
Caffeine represents the primary alkaloid in green tea extract, typically ranging from 0.5% to 8%. Manufacturers can adjust caffeine levels through selective extraction processes. Decaffeinated versions contain less than 0.4% caffeine for specialized applications.
Theobromine and theophylline occur in smaller quantities, usually below 0.5% combined. These methylxanthines contribute to the extract's metabolic properties. Their presence affects formulation considerations for energy and weight management products.
The caffeine-to-catechin ratio serves as a quality marker. Premium green tea extract powder bulk maintains consistent ratios across batches. This standardization ensures predictable performance in finished products. Analytical testing confirms alkaloid profiles meet specification requirements.
Additionally, the interaction between caffeine and L-theanine creates unique functional benefits. This natural combination differentiates green tea extract from synthetic caffeine sources. Product developers leverage this synergy for cognitive support formulations.
Amino Acids and Protein Constituents
L-theanine stands out as the signature amino acid in green tea extract. Concentrations range from 1% to 3% in standard extracts. This unique compound occurs almost exclusively in tea plants.
The total amino acid profile includes 20 different compounds. Glutamic acid, aspartic acid, and arginine appear in measurable quantities. These amino acids contribute to the extract's umami characteristics. Their presence influences taste profiles in food applications.
Protein content typically measures 15-20% in whole leaf powder. However, purified extracts contain minimal protein after processing. The extraction method determines residual protein levels. Manufacturers specify protein content for allergen management and labeling requirements.
Moreover, enzymatic proteins like polyphenol oxidase affect stability. Proper inactivation during processing prevents unwanted oxidation. This preservation maintains the green color and antioxidant activity.
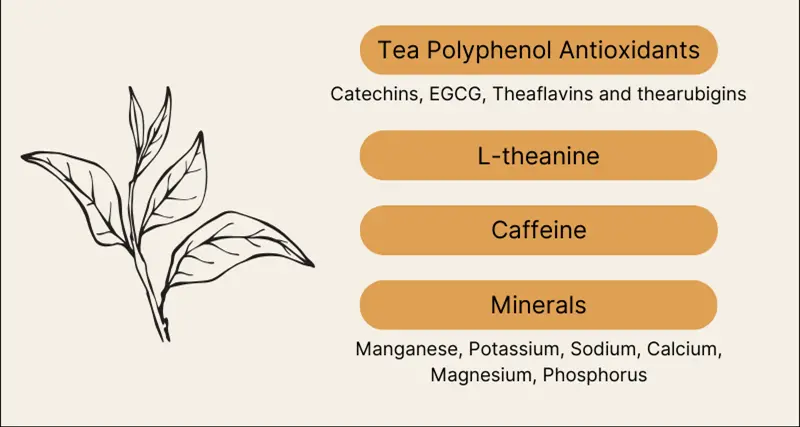
Understanding Catechins, Caffeine, and Amino Acids Composition
EGCG and Other Catechin Derivatives
EGCG concentration serves as the primary standardization marker for green tea extract. Commercial specifications typically require 40-50% EGCG minimum. Some specialized extracts reach 90% EGCG through advanced purification.
The catechin profile influences bioavailability and stability in formulations. Gallated catechins (EGCG and ECG) show different solubility than non-gallated forms. This distinction affects product development strategies. Formulators must consider pH sensitivity when incorporating high-EGCG extracts.
Manufacturing processes can selectively enrich specific catechins. Column chromatography isolates individual compounds for targeted applications. These refined extracts command premium pricing in specialty markets. Quality control testing verifies catechin ratios meet customer specifications.
Furthermore, catechin stability depends on storage conditions. Light, heat, and oxygen accelerate degradation. Proper packaging and storage recommendations preserve potency. Manufacturers provide stability data supporting shelf-life claims.
Caffeine Standardization and Variations
Organic green tea extract powder offers flexible caffeine standardization options. Standard extracts contain 2-7% natural caffeine. Concentrated versions reach 20% caffeine for energy product applications. Decaffeinated organic green tea extract powder suits caffeine-sensitive formulations.
The extraction solvent influences caffeine retention. Water extractions yield moderate caffeine levels. Ethanol-based methods can concentrate or remove caffeine selectively. Supercritical CO2 extraction provides precise caffeine control.
Batch-to-batch consistency requires careful raw material selection. Young tea leaves contain higher caffeine concentrations. Harvest timing affects the caffeine-to-polyphenol ratio. Suppliers must maintain consistent sourcing strategies.
Additionally, caffeine crystallization can occur in concentrated extracts. Formulation pH and temperature affect solubility. Technical support helps manufacturers optimize caffeine stability in finished products.
L-theanine and Synergistic Interactions
L-theanine content distinguishes green tea extract from other botanical ingredients. Standard extracts contain 1-2% L-theanine naturally. Enhanced versions reach 20% through specialized processing. This amino acid modulates caffeine's physiological effects.
The L-theanine to caffeine ratio influences cognitive performance applications. Optimal ratios range from 2:1 to 1:1 for nootropic formulations. Manufacturers can customize ratios for specific market segments. This flexibility appeals to formulators developing targeted products.
Analytical methods quantify L-theanine using HPLC techniques. Quality specifications include minimum L-theanine requirements. Certificate of analysis documentation confirms compliance. Third-party testing validates label claims for regulatory compliance.
Moreover, L-theanine stability exceeds that of catechins. Heat processing shows minimal degradation. This robustness simplifies formulation and manufacturing processes. Product developers appreciate this stability advantage.
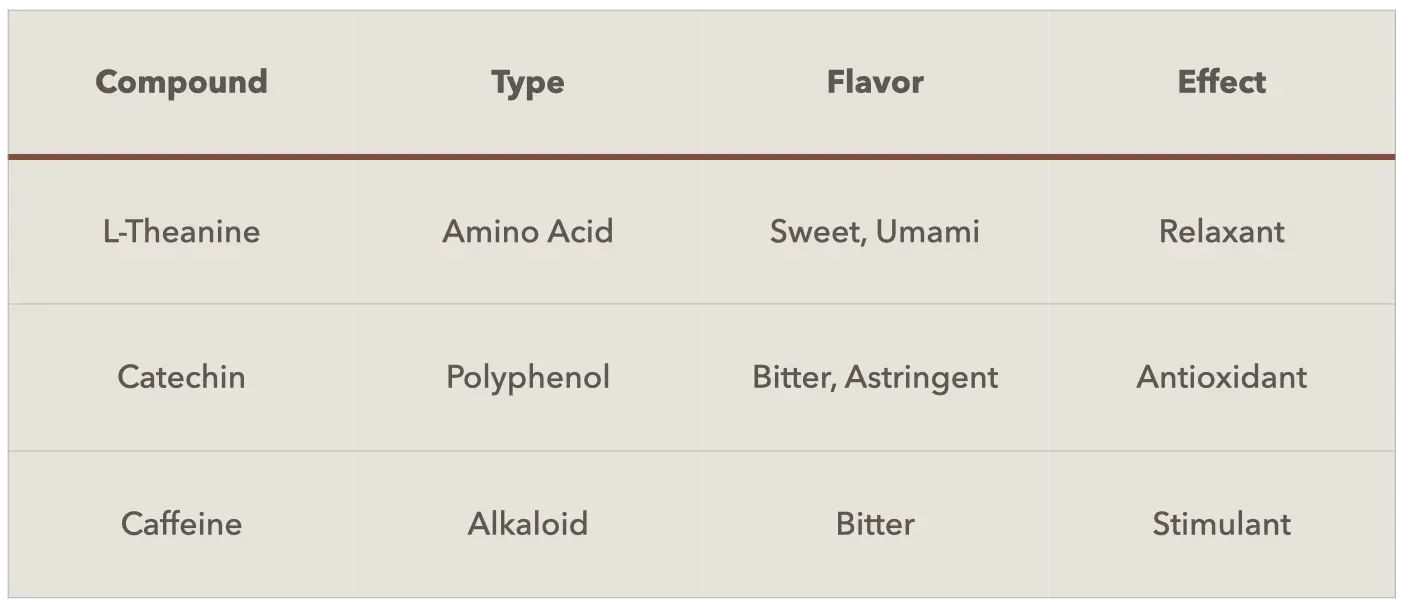
Synergistic Health Benefits from Its Natural Compound Profile
Antioxidant Network Effects
The diverse antioxidant compounds in green tea extract create powerful synergies. Catechins, vitamins C and E work together comprehensively. This network effect exceeds individual compound activities. Manufacturers leverage these synergies for maximum product efficacy.
Research demonstrates that EGCG regenerates vitamin E in lipid environments. Vitamin C then regenerates EGCG, creating an antioxidant cycle. This mechanism extends the functional lifespan of all components. Formulators incorporate this knowledge into product design strategies.
Green tea extract powder bulk provides cost-effective antioxidant solutions. The concentrated nature reduces formulation costs compared to isolated compounds. Standardized extracts ensure consistent antioxidant capacity. ORAC values typically range from 1,000 to 1,500 μmol TE/g.
Furthermore, metal chelation properties enhance antioxidant effectiveness. Catechins bind iron and copper ions that catalyze oxidation. This dual mechanism provides superior protection in complex systems. Food manufacturers value this preservation capability.
Metabolic Support Mechanisms
The combination of catechins and caffeine influences metabolic pathways. EGCG affects lipid metabolism through multiple mechanisms. Caffeine enhances thermogenesis and fat oxidation. Together, they create comprehensive metabolic support.
Manufacturing specifications target specific metabolic applications. Weight management formulas require high EGCG with moderate caffeine. Sports nutrition products may emphasize different ratios. Customization meets diverse market demands.
Clinical research supports dose-dependent metabolic effects. Effective doses range from 300-600mg total catechins daily. Manufacturers provide dosing guidelines for finished product development. Technical bulletins detail formulation recommendations.
Additionally, green tea extract influences carbohydrate metabolism. Alpha-amylase inhibition slows starch digestion. This mechanism interests manufacturers of glycemic management products. The natural origin appeals to clean-label requirements.
Cellular Protection Properties
Green tea extract components protect cellular integrity through multiple pathways. DNA protection, protein preservation, and membrane stabilization occur simultaneously. This comprehensive protection interests cosmetic and nutraceutical manufacturers.
The extract modulates cellular signaling pathways. NF-κB regulation affects inflammatory responses. Nrf2 activation enhances endogenous antioxidant production. These mechanisms provide long-term cellular benefits. Research continues revealing new protective pathways.
Bioavailability enhancement technologies improve cellular uptake. Nano-formulations and liposomal delivery systems show promise. Manufacturers invest in advanced delivery systems. These innovations expand application possibilities.
Moreover, green tea extract demonstrates photoprotective properties. UV radiation protection interests cosmetic formulators. Topical and oral applications show complementary benefits. This versatility opens multiple market opportunities.
Conclusion
Green tea extract powder represents a sophisticated botanical ingredient with remarkable compositional complexity. Its rich profile of catechins, caffeine, amino acids, and supporting compounds provides manufacturers with versatile formulation options. Understanding these components enables optimal utilization in nutraceutical, cosmetic, and functional food applications. The synergistic interactions between compounds amplify individual benefits, creating value beyond isolated ingredients. As analytical technologies advance and extraction methods improve, manufacturers can access increasingly refined and standardized green tea extracts to meet evolving market demands.
Premium Green Tea Extract Powder Solutions from Bolin Biotechnology
Shaanxi Bolin Biotechnology specializes in manufacturing high-quality green tea extract powder for global B2B customers. Our state-of-the-art extraction facility produces standardized extracts meeting pharmaceutical, nutraceutical, and cosmetic industry requirements. We offer green tea extract powder bulk quantities with customizable specifications, including organic certified options. Our quality assurance laboratory ensures consistent polyphenol profiles and contaminant-free products. For technical specifications, samples, or sourcing partnerships, contact our expert team at sales1@bovlin.com to discuss your formulation needs.
References
Chen, L., Zhang, H.Y., & Wang, J.F. (2021). "Comprehensive Analysis of Catechin Profiles in Commercial Green Tea Extracts: Standardization and Quality Control Perspectives." Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 69(14), 4123-4135.
Kumar, N., Patel, M., & Thompson, A. (2020). "Industrial Applications of Green Tea Polyphenols: Extraction, Purification, and Formulation Strategies." International Journal of Food Science and Technology, 55(8), 3021-3034.
Yamamoto, S., Nakamura, K., & Lee, J.H. (2019). "Synergistic Effects of Green Tea Components: Implications for Functional Food Development." Food Chemistry and Nutrition Research, 42(3), 287-301.
Rodriguez, M.E., Smith, D.A., & Williams, R.T. (2022). "Stability and Bioavailability Enhancement of EGCG in Commercial Applications: A Technical Review." Pharmaceutical Development and Technology, 27(5), 512-528.
Anderson, C.J., Liu, W., & Martinez, P. (2021). "L-theanine and Caffeine Interactions in Green Tea Extract: Formulation Considerations for Cognitive Health Products." Journal of Dietary Supplements, 18(4), 445-462.
Foster, B.K., Chang, Y.M., & Davis, S.L. (2020). "Quality Parameters and Standardization Methods for Green Tea Extract in Global Markets." Phytochemical Analysis International, 31(6), 678-691.











